外部开发模式
这段代码是一个 DLL(动态链接库)中的函数,该函数用于调用另一个可执行文件(EXE)并传递参数。
首先,它定义了一个名为 CallExeAndPassParameters 的函数,并使用 __declspec(dllexport) 将其声明为导出函数,以便其他程序可以调用。
在函数内部,它设置了要调用的 EXE 文件路径(exePath)和要传递的参数值(parameter1、parameter2 和 parameter3)。然后,它通过将这些值拼接到一起来构建命令行字符串(commandLine),以便将其作为参数传递给 CreateProcess 函数。
接下来,它创建了进程的结构体(STARTUPINFO 和 PROCESS_INFORMATION),并使用 CreateProcess 函数启动了一个新的进程,即要调用的 EXE 程序。传递给 CreateProcess 的参数包括命令行字符串和其他必要的参数。
如果 CreateProcess 成功启动了进程,那么它会等待进程结束(WaitForSingleObject)并关闭进程和线程句柄(CloseHandle)。
总之,这段代码的作用是通过 DLL 调用一个指定路径的 EXE 文件,并将参数传递给该 EXE 程序。
演示
演示中主线程调用完后,不等待子线程接触,直接将主线程结束
代码
注意,在调用 CreateProcess 函数之前,需要将命令行字符串转换为 wchar_t* 类型
cpp
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
// 可变参数函数,用于将不定数量和类型的参数转换为命令行字符串
std::wstring BuildCommandLine(const wchar_t* exePath, ...)
{
std::wstringstream commandLineStream;
commandLineStream << L"\"" << exePath << L"\"";
va_list args;
va_start(args, exePath);
const wchar_t* arg = va_arg(args, const wchar_t*);
while (arg != nullptr)
{
commandLineStream << L" \"" << arg << L"\"";
arg = va_arg(args, const wchar_t*);
}
va_end(args);
return commandLineStream.str();
}
int main()
{
const wchar_t* exePath = L"path_to_your_exe.exe";
const wchar_t* parameter1 = L"Value 1";
const wchar_t* parameter2 = L"Value 2";
const wchar_t* parameter3 = L"Value 3";
// 构建命令行字符串
std::wstring commandLine = BuildCommandLine(exePath, parameter1, parameter2, parameter3, nullptr);
// 创建进程的结构体
STARTUPINFO si;
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi;
// 清空结构体
ZeroMemory(&si, sizeof(si));
si.cb = sizeof(si);
ZeroMemory(&pi, sizeof(pi));
// 启动可执行文件进程并传递参数
if (CreateProcess(NULL, const_cast<wchar_t*>(commandLine.c_str()), NULL, NULL, FALSE, 0, NULL, NULL, &si, &pi))
{
// 等待进程结束
WaitForSingleObject(pi.hProcess, INFINITE);
// 关闭进程句柄
CloseHandle(pi.hProcess);
CloseHandle(pi.hThread);
}
else
{
std::cout << "无法启动进程:" << GetLastError() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
改造成多线程
由于运行速度较慢,等程序进行优化
在这个修改后的代码中,我们使用 std::thread 来创建一个子线程来执行可执行文件。主线程在启动子线程后继续执行其他操作,而不需要等待子线程完成。当子线程执行完毕后,它会发送通知给主线程,然后主线程可以继续执行后续操作。
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <thread>
// 可变参数函数,用于将不定数量和类型的参数转换为命令行字符串
std::wstring BuildCommandLine(const wchar_t* exePath, ...)
{
std::wstringstream commandLineStream;
commandLineStream << L"\"" << exePath << L"\"";
va_list args;
va_start(args, exePath);
const wchar_t* arg = va_arg(args, const wchar_t*);
while (arg != nullptr)
{
commandLineStream << L" \"" << arg << L"\"";
arg = va_arg(args, const wchar_t*);
}
va_end(args);
return commandLineStream.str();
}
// 子线程函数,用于启动可执行文件进程并传递参数
void ExecuteProcess(const wchar_t* commandLine)
{
// 创建进程的结构体
STARTUPINFO si;
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi;
// 清空结构体
ZeroMemory(&si, sizeof(si));
si.cb = sizeof(si);
ZeroMemory(&pi, sizeof(pi));
// 启动可执行文件进程并传递参数
if (CreateProcess(NULL, const_cast<wchar_t*>(commandLine), NULL, NULL, FALSE, 0, NULL, NULL, &si, &pi))
{
// 等待进程结束
WaitForSingleObject(pi.hProcess, INFINITE);
// 关闭进程句柄
CloseHandle(pi.hProcess);
CloseHandle(pi.hThread);
// 发送通知给主线程
std::cout << "子进程执行完毕,可以进行后续操作" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "无法启动进程:" << GetLastError() << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
const wchar_t* exePath = L"path_to_your_exe.exe";
const wchar_t* parameter1 = L"Value 1";
const wchar_t* parameter2 = L"Value 2";
const wchar_t* parameter3 = L"Value 3";
// 构建命令行字符串
std::wstring commandLine = BuildCommandLine(exePath, parameter1, parameter2, parameter3, nullptr);
// 创建子线程来执行可执行文件
std::thread workerThread(ExecuteProcess, commandLine.c_str());
// 主线程继续执行其他操作
std::cout << "主线程继续执行其他操作" << std::endl;
// 等待子线程执行完毕
workerThread.join();
return 0;
}
改造成异步执行
主线程不需要等待子线程完成,可以考虑使用C++中的异步编程模型,如std::async和std::future。这样可以更灵活地控制异步任务的执行,并获取任务的结果。
我们使用std::async来创建一个异步任务,并将ExecuteProcess函数作为参数传递进去。std::launch::async参数表示任务应该立即启动执行。
主线程在启动异步任务后可以继续执行其他操作,而不需要等待异步任务完成。如果需要获取异步任务的结果,可以使用future.get()方法,它会阻塞主线程,直到异步任务完成并返回结果。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <future>
#include <Windows.h>
void ExecuteProcess(const wchar_t* commandLine)
{
STARTUPINFO startupInfo = { sizeof(startupInfo) };
PROCESS_INFORMATION processInfo;
// 启动进程
if (CreateProcess(nullptr, const_cast<wchar_t*>(commandLine), nullptr, nullptr, FALSE, 0, nullptr, nullptr, &startupInfo, &processInfo))
{
// 等待进程结束
WaitForSingleObject(processInfo.hProcess, INFINITE);
// 获取进程退出码
DWORD exitCode;
GetExitCodeProcess(processInfo.hProcess, &exitCode);
// 关闭句柄
CloseHandle(processInfo.hProcess);
CloseHandle(processInfo.hThread);
// 打印进程退出码
std::cout << "子进程退出码:" << exitCode << std::endl;
}
else
{
// 创建进程失败
std::cerr << "无法创建进程" << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
const wchar_t* exePath = L"path_to_your_exe.exe";
const wchar_t* parameter1 = L"Value 1";
const wchar_t* parameter2 = L"Value 2";
const wchar_t* parameter3 = L"Value 3";
// 构建命令行字符串
std::wstring commandLine = BuildCommandLine(exePath, parameter1, parameter2, parameter3, nullptr);
// 异步执行子线程
std::async(std::launch::async, ExecuteProcess, commandLine.c_str());
// 主线程继续执行其他操作
std::cout << "主线程继续执行其他操作" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
不等待子线程结束的多线程操作
异步执行ExecuteProcess函数而不等待其完成,可以使用std::thread来创建一个单独的线程来执行该函数。
使用std::thread创建一个单独的线程来执行ExecuteProcess函数,并通过调用thread.detach()将线程与主线程分离,使其自行运行而不会阻塞主线程。
注意,如果主线程提前退出,子线程可能会被强制终止,因此请确保主线程不会过早退出,以免影响子线程的执行。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <Windows.h>
void ExecuteProcess(const wchar_t* commandLine)
{
STARTUPINFO startupInfo = { sizeof(startupInfo) };
PROCESS_INFORMATION processInfo;
// 启动进程
if (CreateProcess(nullptr, const_cast<wchar_t*>(commandLine), nullptr, nullptr, FALSE, 0, nullptr, nullptr, &startupInfo, &processInfo))
{
// 关闭句柄,不等待进程结束
CloseHandle(processInfo.hProcess);
CloseHandle(processInfo.hThread);
}
else
{
// 创建进程失败
std::cerr << "无法创建进程" << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
const wchar_t* exePath = L"path_to_your_exe.exe";
const wchar_t* parameter1 = L"Value 1";
const wchar_t* parameter2 = L"Value 2";
const wchar_t* parameter3 = L"Value 3";
// 构建命令行字符串
std::wstring commandLine = BuildCommandLine(exePath, parameter1, parameter2, parameter3, nullptr);
// 异步执行子线程
std::thread thread(ExecuteProcess, commandLine.c_str());
// 分离线程,使其自行运行
thread.detach();
// 主线程继续执行其他操作
std::cout << "主线程继续执行其他操作" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
在NXOpen中的具体实现
被调用的exe项目
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Do something
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
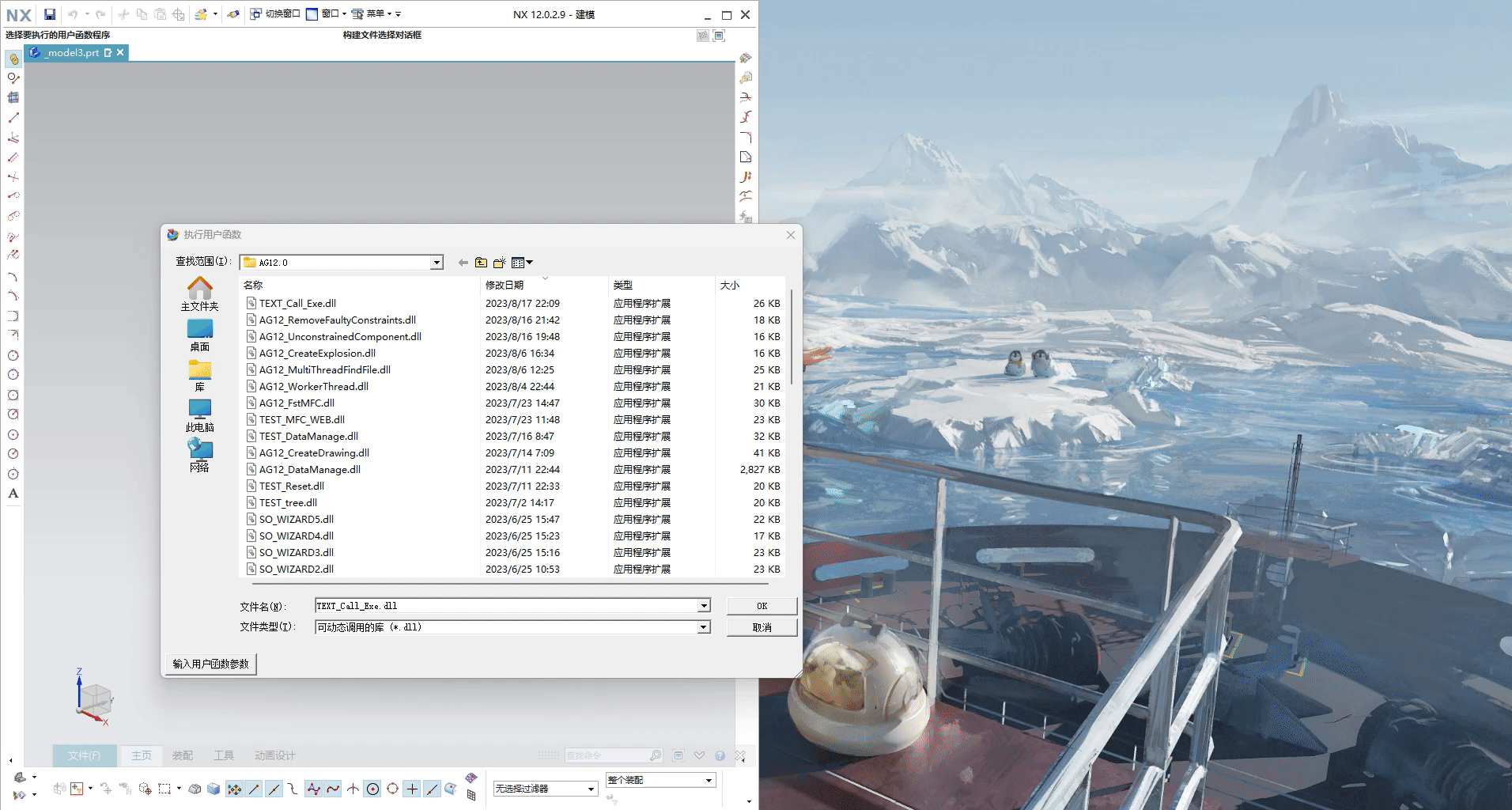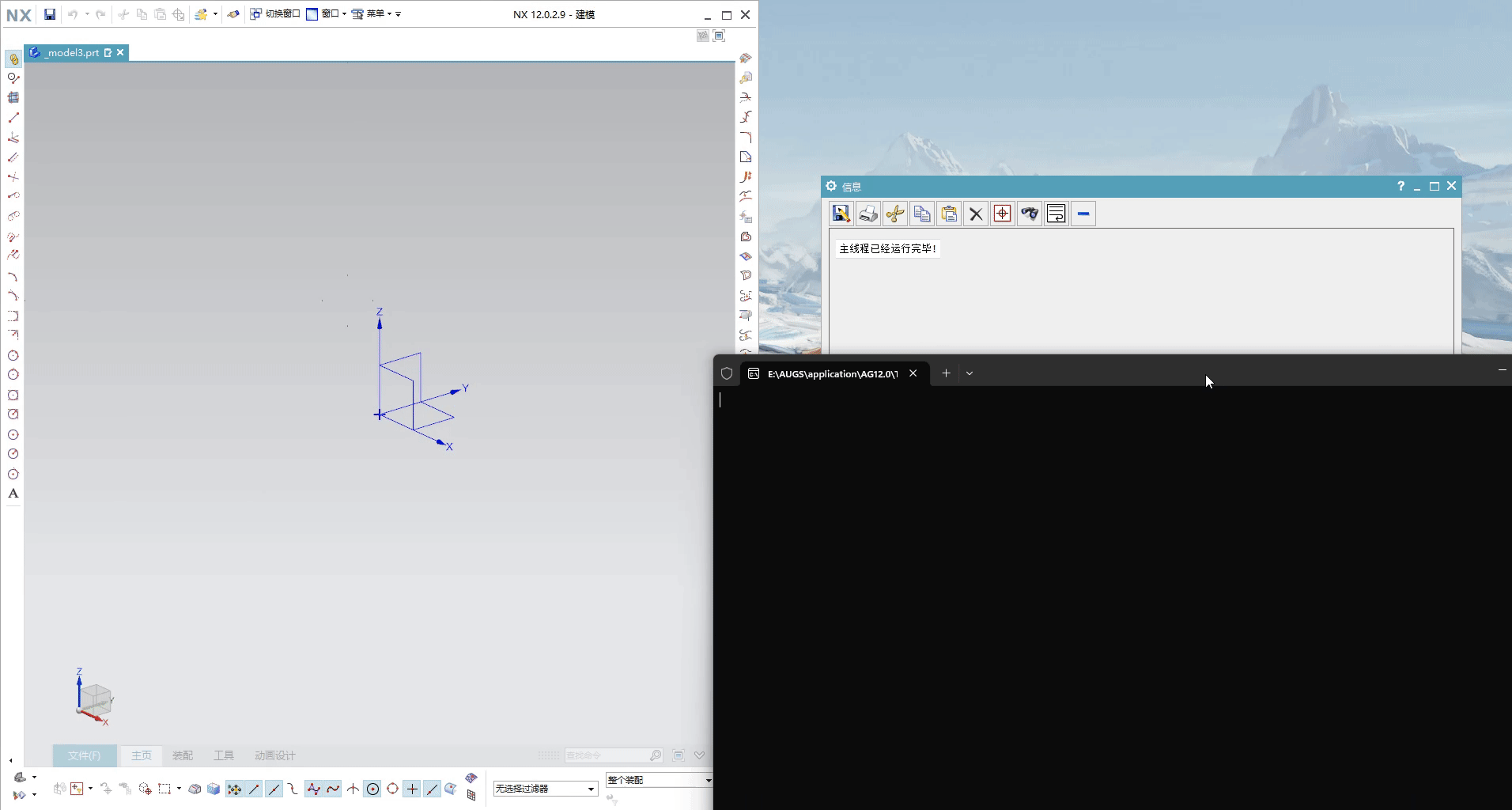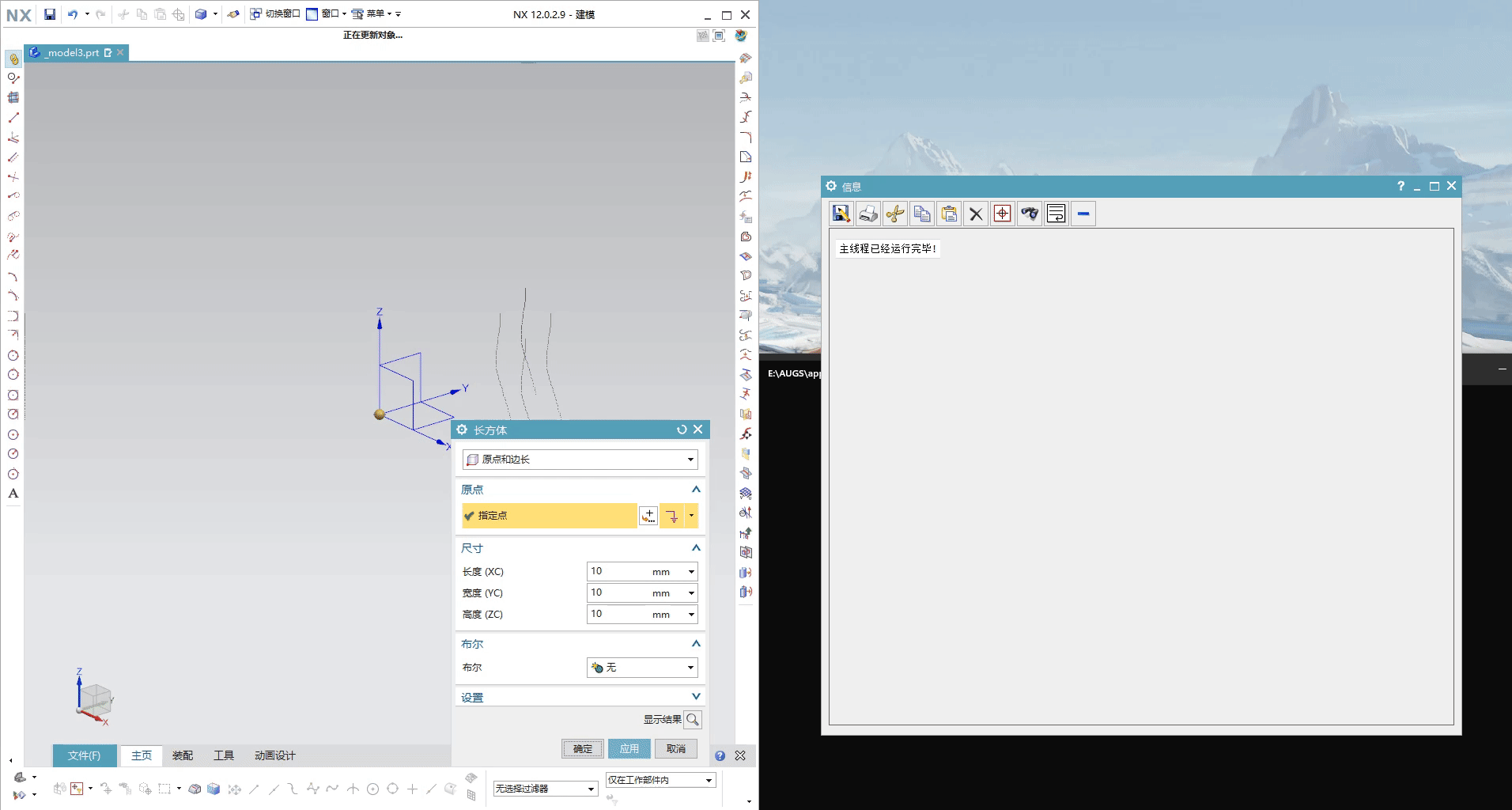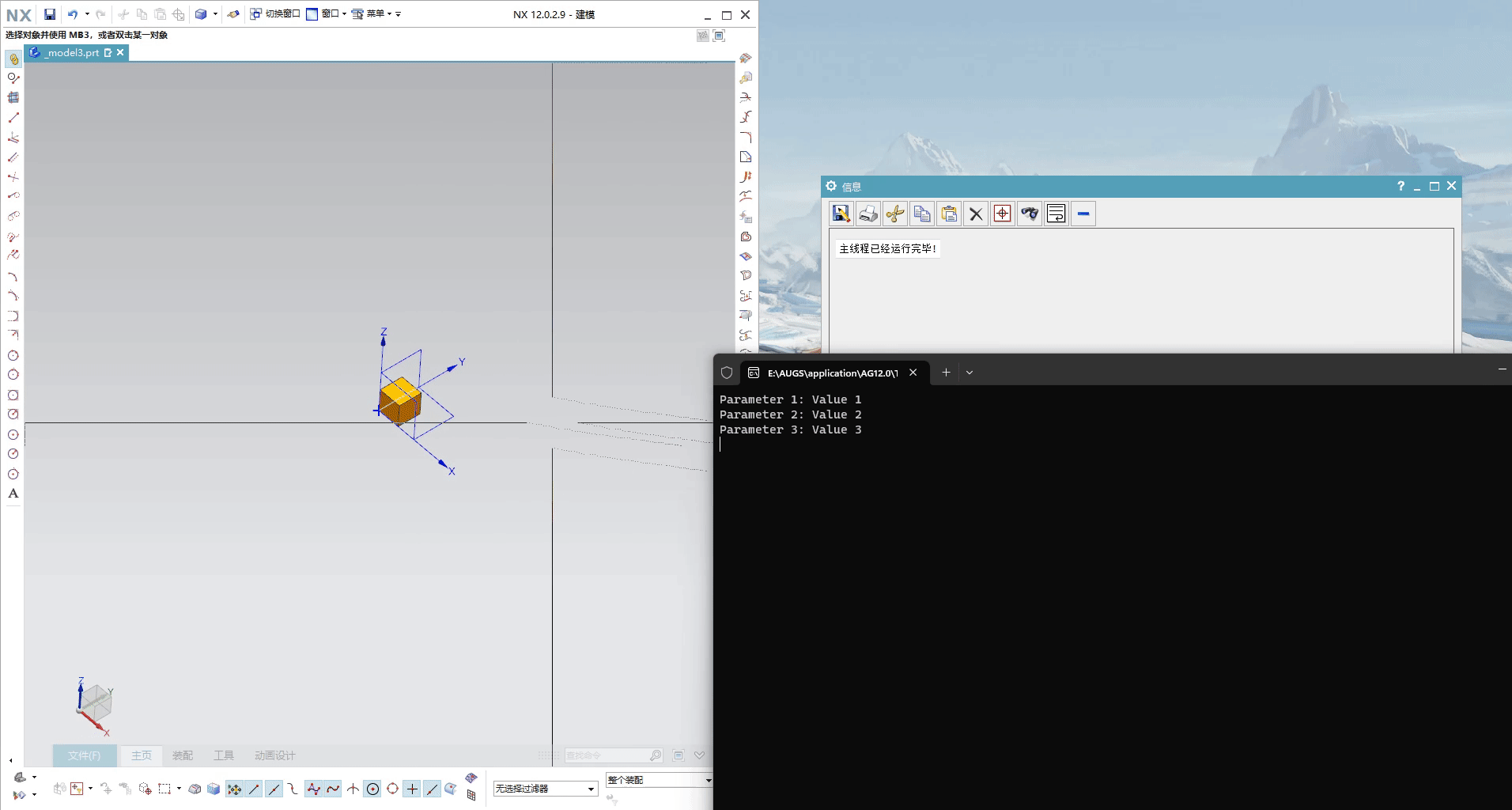
void TEXTBlock::do_it(const char* parameter1, const char* parameter2, const char* parameter3)
{
// 在这里进行处理
std::cout << "Parameter 1: " << parameter1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "Parameter 2: " << parameter2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "Parameter 3: " << parameter3 << std::endl;
getchar();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Entry point for unmanaged external NXOpen C/C++ programs
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
try
{
// Create NXOpen C++ class instance
TEXTBlock* theTEXTBlock;
theTEXTBlock = new TEXTBlock();
if (argc > 1)
{
theTEXTBlock->do_it(argv[1], argv[2], argv[3]);
}
delete theTEXTBlock;
}
catch (const NXException& e1)
{
cerr << "NXException: " << e1.ErrorCode() << endl;
cerr << e1.Message() << endl;
}
catch (const exception& e2)
{
cerr << "Exception: " << e2.what() << endl;
}
catch (...)
{
cerr << "Unknown Exception: " << endl;
}
}
使用dll对exe进行传递参数的项目
void execute_process(const wchar_t* commandLine)
{
STARTUPINFO startupInfo = { sizeof(startupInfo) };
PROCESS_INFORMATION processInfo;
// 启动进程
if (CreateProcess(nullptr, const_cast<wchar_t*>(commandLine), nullptr, nullptr, FALSE, 0, nullptr, nullptr, &startupInfo, &processInfo))
{
// 关闭句柄,不等待进程结束
CloseHandle(processInfo.hProcess);
CloseHandle(processInfo.hThread);
}
else
{
// 创建进程失败
std::cerr << "无法创建进程" << std::endl;
}
}
std::wstring MyClass::build_command_line(const wchar_t* exe_path, ...)
{
std::wstringstream commandLineStream;
commandLineStream << L"\"" << exe_path << L"\"";
va_list args;
va_start(args, exe_path);
const wchar_t* arg = va_arg(args, const wchar_t*);
while (arg != nullptr)
{
commandLineStream << L" \"" << arg << L"\"";
arg = va_arg(args, const wchar_t*);
}
va_end(args);
return commandLineStream.str();
}
void MyClass::do_it()
{
// TODO: add your code here
const wchar_t* exePath = L"E:\\AUGS\\application\\AG12.0\\TEXT_Block.exe";
//const char* exePath = "path_to_your_exe.exe";
const wchar_t* parameter1 = L"Value 1";
const wchar_t* parameter2 = L"Value 2";
const wchar_t* parameter3 = L"Value 3";
// 构建命令行字符串
std::wstring commandLine = build_command_line(exePath, parameter1, parameter2, parameter3, nullptr);
//// 异步执行子线程
//std::future<void> future = std::async(std::launch::async, execute_process, commandLine.c_str());
// 创建新线程执行子进程
std::thread thread(execute_process, commandLine.c_str());
// 分离线程,使其自行运行
thread.detach();
print("主线程已经运行完毕!");
}





评论区